Typical/Atypical Development
Infant Reflexes and Possible Effects if Reflex Persists Abnormally
Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (ATNR)
Stimulus- Head position; Turned to one side
Response- Arm and Leg on Face side are extended; Arm and leg on scalp are flexed; Spine curved with convexity toward face side
Normal age of response- Birth to 6 months
Interferes with- Feeding; Visual tracked; Midline use of hands; Bilateral hand use; Rolling; Development of crawling; can lead to skeletal deformities (e.g., scoliosis, hip subluxation, hip dislocation)
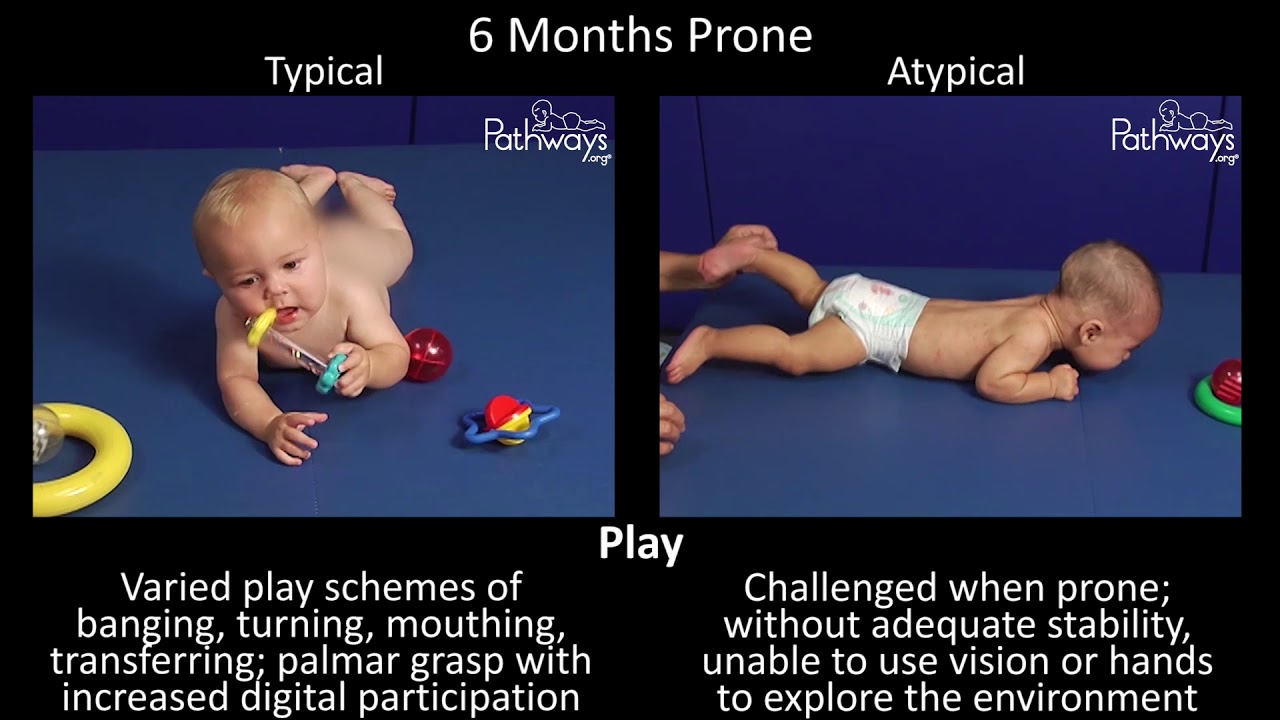
Symmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (STNR)
Stimulus- Head position, flexion, or extension
Response- When head is in flex, arms are flexed, legs extended
Normal age of response- 6 to 8 months
Interferes with- Ability to prop on arms in prone position; Attaining and maintaining hands-and-knees position; Crawling reciprocally; Sitting balance when looking around; use of hands when looking around; Use of hands when looking at objects in hands in sitting position
Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR)
Stimulus- Position of labyrinth in inner ear, reflected in head position
Response- In the supine position, body and extremities are held in extension; In the prone position, body and extremities are held in flexion
Normal age of response- Birth to 6 months
Interferes with-Ability to initiate rolling; Ability to prop on elbows with extended hips when prone; Ability to flex trunk and hips to come to sitting position from supine position; Often causes full body extension, which interferes with balance in sitting or standing.
Galant Reflex
Stimulus- Touch to skin along spine form shoulder to hip
Response- Lateral flexion of trunk to side stimulus
Normal age of response- 30 weeks of gestation to 2 months
Interferes with- Development of sitting balance; Can lead to scoliosis
Palmar Grasp Reflex
Stimulus- Pressure in the palm on the ulnar side of hand
Response- Flexion of fingers causing strong grip
Normal age of response- Birth to 4 months
Interferes with- Ability to grasp and release objects voluntarily; Weight bearing on open hand for propping, crawling, protective responses
Plantar Grasp Reflex
Stimulus- Pressure to base of toes
Response- Toe flexion
Normal age of response- 28 weeks of gestation to 9 months
Interferes with- Ability to stand with feet flat on surface; Balance reactions and weight shifting in standing
Rooting Reflex
Stimulus- Touch on cheek
Response- Turning head to same side with mouth open
Normal age of response- 28 weeks of gestation to 3 months
Interferes with- Oral-motor development; Development of midline control of head; Optical righting, visual tracking, and social interaction
Moro Reflex
Stimulus- Head dropping into extension suddenly for a few inches
Response- Arms abduct with fingers open, then cross trunk in to adduction, cry
Normal are of response- 28 weeks to 5 months
Interferes with- Balance reaction in sitting; Protective responses in sitting; Eye-hand coordination, visual tracking
Startle Reflex
Stimulus- Loud, sudden noise
Response- Similar to Moro response, but elbows remains flexed and hands closed
Normal are of response- 28 weeks of gestation to 5 months
Interferes with- Sitting balance; protective responses in sitting; Eye-hand coordination, visual tracking; social interaction, attention
Positive Support Reflex
Stimulus- Weight placed on balls of feet when upright
Response- Stiffening of legs and trunk into extension
Normal age of response- 35 weeks of gestation to 2 months
Interferes with- Standing and walking; balance reactions and weight shift in standing; Can lead to contractures of ankles into plantar flexion
Walking (stepping) Reflex
Stimulus- Supported upright position with soles of feet on firm surface
Response- Reciprocal flexion/extension of legs
Normal age of response- 38 week of gestation to 2 months
Interferes with- Standing and walking; balance reactions and weight shifting in standing; Development of smooth, coordinated reciprocal movements of lower extremities
Giles S. PTAEXAM. Scarborough: Scorebuilders; 2020:277-278.